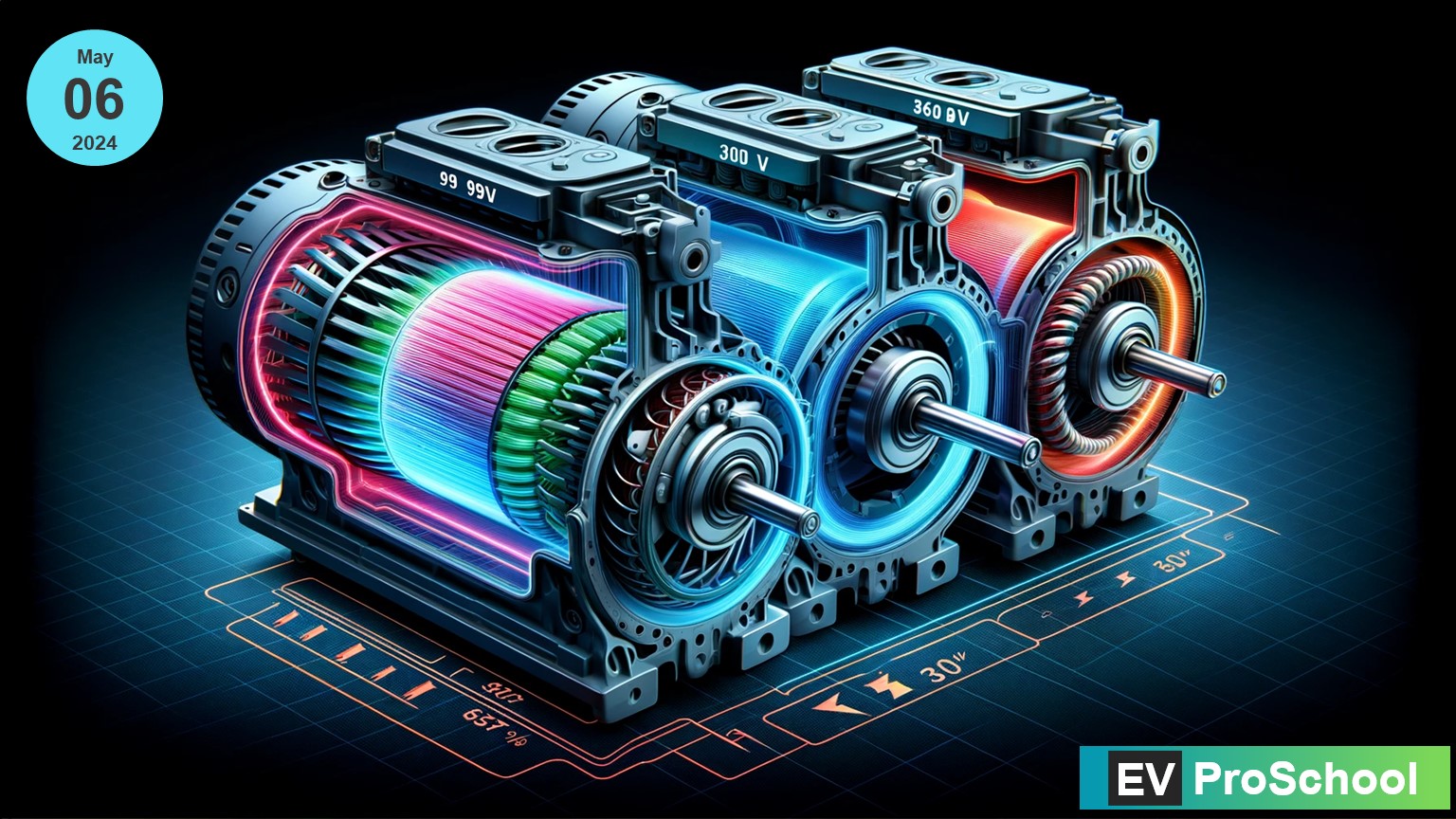
In the ever-evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), understanding the impact of voltage changes on electric motor windings is crucial for both designers and enthusiasts alike. As the voltage increases from 96V to 330V, and further to 660V, the design and performance of electric motors undergo significant transformations. These changes not only affect the efficiency and power output of the motor but also its thermal stability and durability. This blog post delves into the technicalities of these voltage shifts, exploring their implications on motor windings and how they revolutionize EV performance, with a special focus on the Indian market.
The Science Behind Voltage and Motor Windings
Electric motors are the heart of EVs, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. The winding within the motor plays a pivotal role in this conversion process. As we increase the operating voltage from 96V to 330V and then to 660V, several key changes occur in the motor winding design and materials:
- Wire Gauge and Winding Turns: Higher voltages require thinner wire gauges due to decreased current for the same power output, reducing the ohmic losses. This allows for more turns in the winding, increasing the motor’s efficiency.
- Insulation Requirements: Increased voltage demands better insulation to prevent dielectric breakdown. Materials with higher dielectric strength become necessary to ensure safety and reliability.
- Thermal Management: Higher voltages lead to improved efficiency, which can lower the heat generated. However, the design must also consider the potential for localized hot spots and ensure adequate cooling mechanisms.
- Material Considerations: The materials used in the windings must have a high thermal conductivity and be resistant to higher electrical stresses. Copper remains the preferred choice, but the purity and the alloy composition might be optimized for higher voltages.
Practical Implications for EVs in India
The shift towards higher voltages in EVs brings about several advantages, particularly for the Indian market:
- Increased Efficiency: Higher voltage levels lead to lower losses and increased motor efficiency, crucial for extending the driving range of EVs, a key concern among Indian consumers.
- Compact Design: Motors designed for higher voltages can be more compact due to reduced winding copper weight, contributing to lighter and more space-efficient vehicles.
- Improved Performance: Higher voltages enable quicker acceleration and better hill-climbing capabilities, appealing to the performance expectations of Indian drivers.
- Charging Speed: Vehicles operating at higher voltages can leverage faster charging technologies, reducing downtime and making EVs more practical for Indian users.

Challenges and Solutions
The transition to higher voltage systems is not without its challenges. Safety concerns, cost implications, and the need for upgraded infrastructure must be addressed. Innovations in insulation technology, the development of cost-effective high-voltage components, and the expansion of high-voltage charging networks in India are crucial steps forward.
Conclusion
Increasing the voltage in electric vehicle motors from 96V to 330V and then to 660V represents a significant leap towards enhancing EV performance, efficiency, and suitability for the Indian market. While challenges remain, the advancements in motor winding technology and materials, combined with supportive policies and infrastructure development, pave the way for a bright future for EVs in India.
Further Reading
For those interested in diving deeper into the technicalities of electric motor design and the future of EVs, resources such as the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) India, the Electric Vehicle Association of India (EVAI), and various research papers on electric motor innovations are invaluable.